Top Notch Tips About How To Reduce Copper Oxide With Carbon
At the same time, copper oxide is reduced because oxygen is removed from it.
How to reduce copper oxide with carbon. Weigh the reduction tube empty. In this reaction, carbon is oxidised because it gains oxygen. As such, on a molar basis, the intrinsic chemical reactivity of cuo (or cu 2 o) to co (the rate of oxidation of co by the copper oxide) is given by (6) r ^ copper oxide ″ = r ^.
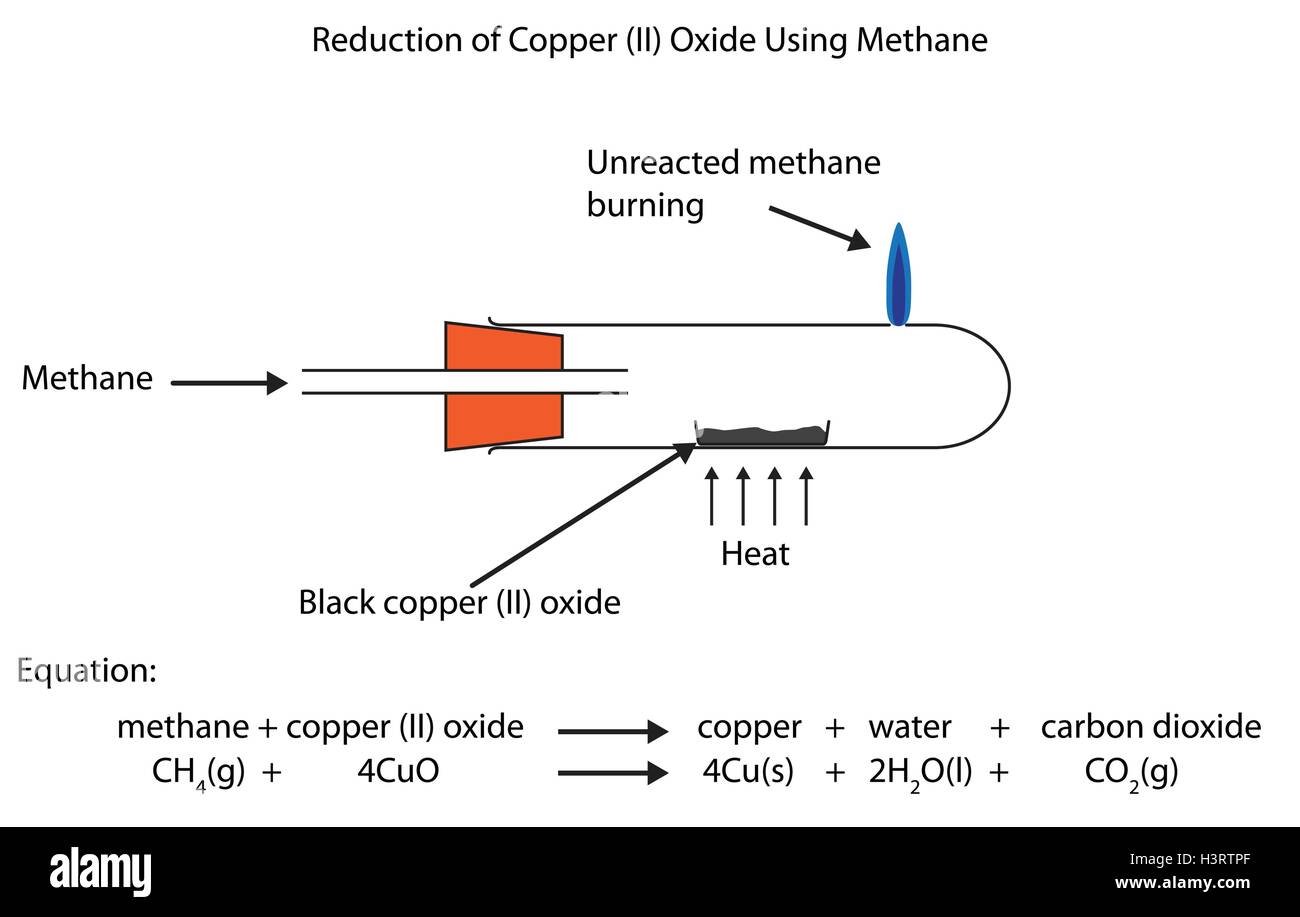
Reduction of copper oxide black copper oxide and black carbon powder are mixed together and heated up. Black copper oxide and black carbon powder are mixed together and heated up. Exposure to oxygen results in the.
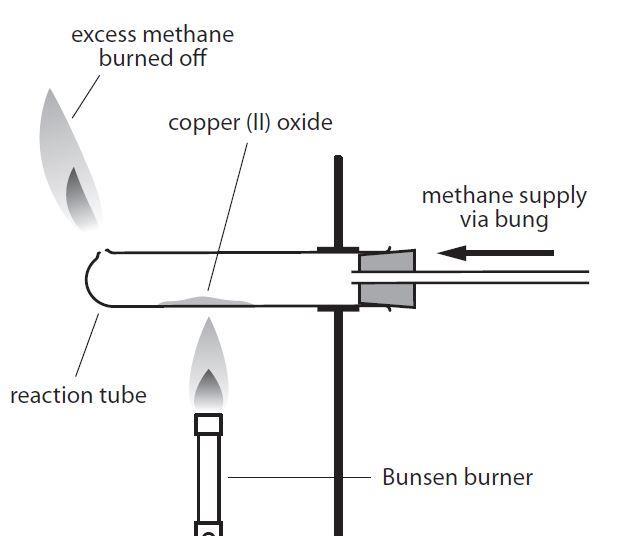
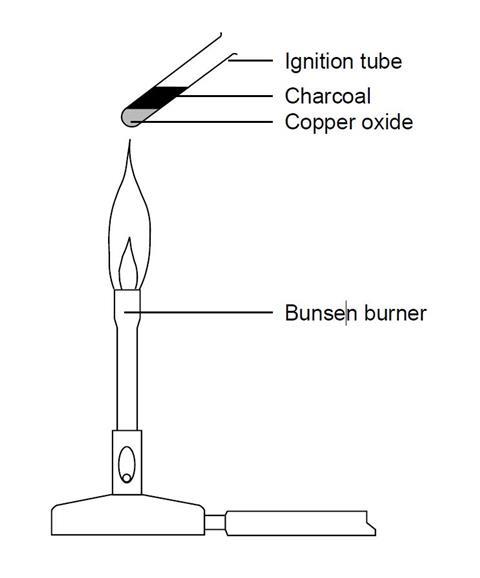
Light the bunsen burner and with the tip of a roaring flame heat the oxide at one end of the pile. The gas evolved is passed into a solution of calcium hydroxide. Chase this glow along the tube.
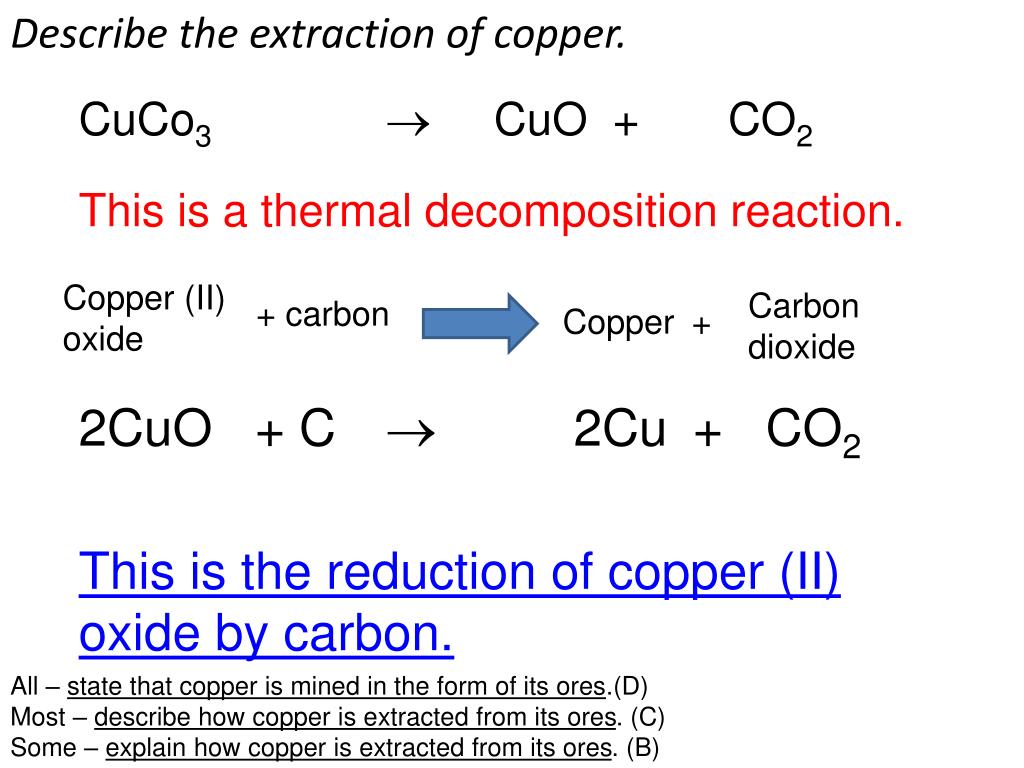
The reactions confirm the place of carbon in the reactivity series, above lead and copper, as it reduces the metal oxides to the metals and is itself oxidised to carbon dioxide: Cuo (s) + c (s) [tex]\rightarrow[/tex] cu (s) + co (s). A faster and cooler way to reduce our carbon footprint.
Answered jan 16, 2018 by faiz (314k points) selected jan 25, 2018 by vikash kumar. C is a strong reducing agent and can reduce cuo as. Place about 3 g of copper (ii) oxide along the base of the tube so that it is spread out on the middle of the tube.
Ca is much more reactive than cu and has greater affinity for oxygen than c. Cuo (s) + c (s). C is strong reducing agent and can reduce cuo as follows: